A Simple Guide to Understanding 99% of Specialty Coffee Methods

Understanding the Structure of Coffee Beans
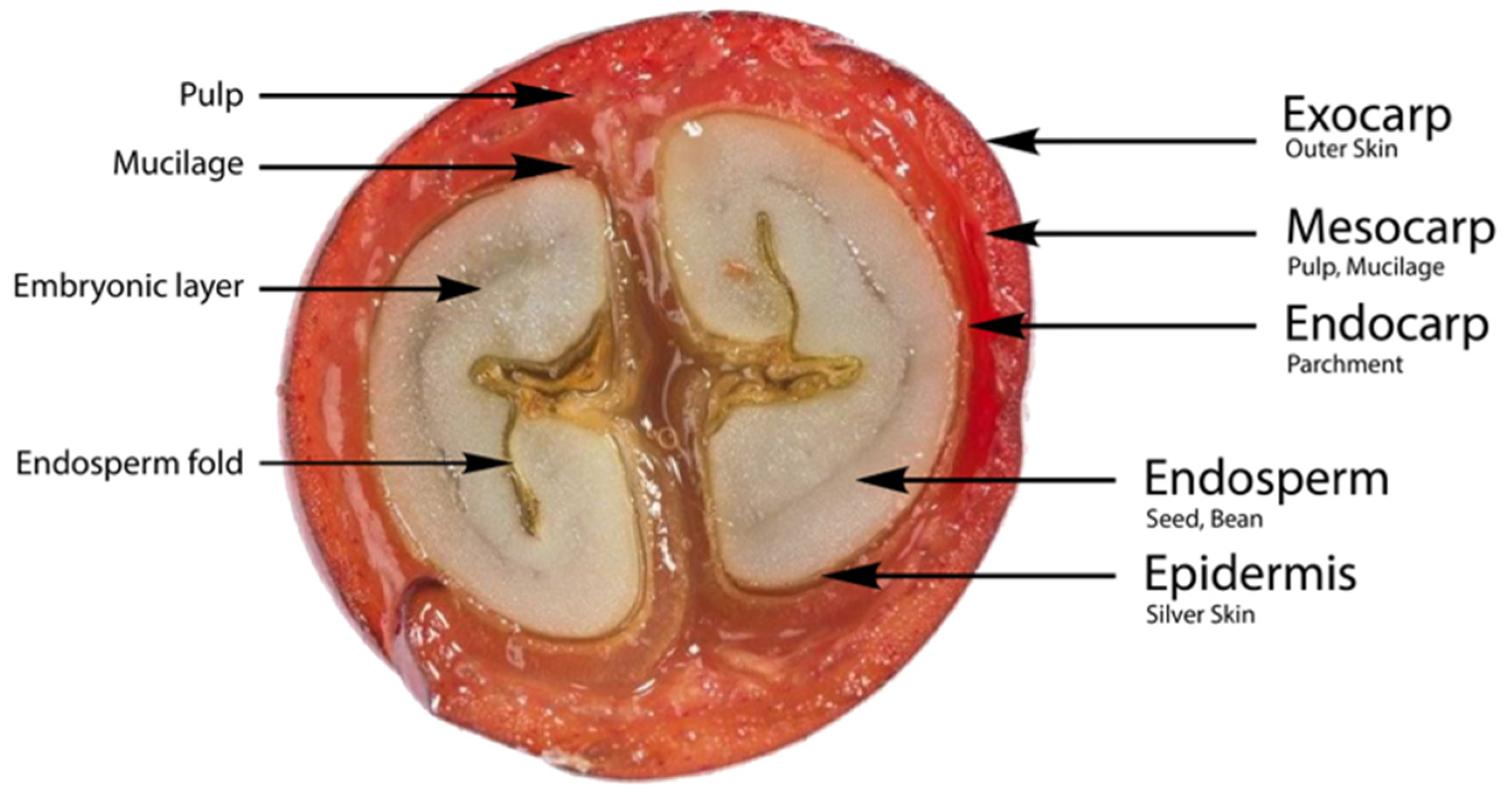
Coffee cherries, just like regular fruits, have several layers: the outer skin, pulp, mucilage, parchment, silver skin, and the seed (coffee bean). Before delving into coffee bean processing methods, it's essential to familiarize ourselves with the different parts of a coffee bean.
-
Outer Skin - The primary function of the outer skin is to protect the coffee cherry.
-
Pulp - The mature outer skin and pulp attract animals for consumption, helping to strip the seeds.
-
Mucilage - Located beneath the pulp, the mucilage is a sticky layer containing sugars.
-
Parchment - Below the mucilage, the parchment is a fibrous shell that encases the seeds.
-
Silver Skin - The thin membrane inside the parchment has a silver color and is shed during coffee roasting.
-
Seed (Coffee Bean) - After undergoing the processing methods, it becomes the green coffee bean ready for roasting.
What is Coffee Bean Processing All About?
Coffee bean processing is the method of extracting coffee seeds from the coffee cherry. To produce the coffee we drink, we only need the seeds, so there are many steps involved in the process. Apart from removing the unnecessary parts, it is essential to consider the preservation time of coffee beans, which requires drying the moisture content to around 12%. Through research, it has been discovered that different processing methods have a significant impact on the flavor of coffee beans. In pursuit of better coffee, many people have devoted themselves to researching and developing various systematic processing methods.
Basic Process of Coffee Bean Processing
In fact, the labels you see on coffee beans in the market are abbreviations of the coffee processing procedures. As the impact of coffee bean processing on the flavor of coffee beans becomes more significant, and companies want to sell their coffee beans at higher prices, they simply put all the distinctive processing methods on the labels to make the processing methods seem impressive and difficult to understand. But in reality, once you understand the context of coffee bean processing, you will actually have a clearer understanding of the processes the coffee beans have gone through. Don't worry about it being difficult to understand; just follow my method, and you will quickly unravel the puzzle of these lengthy processing methods.
The coffee bean processing system can be divided into the following 5 stages:
- Harvesting stage
- Washing stage
- Processing stage
- Fermentation stage
- Drying stage
Each of these stages serves different purposes, all aimed at ultimately extracting the coffee seeds. The secrets that influence the flavor of coffee lie within these processing methods.
Harvesting Stage: Harvesting ripe fruits
In theory, it should be ideal to harvest fully ripe and intact fruits. However, in practice, it is challenging to achieve because it is difficult to establish a uniform standard for fruit ripeness. For example, there are fruits that have just turned red, fruits that have turned red but are still hard, and fruits that have turned red and are fully ripe and soft. There will inevitably be differences in ripeness, making it a challenge to select the right ones. Coffee beans that are not labeled as "harvested from ripe fruits" may not necessarily be harvested from unripe fruits; it could be that it is already assumed to select ripe fruits, or there are other more critical processing procedures that need to be indicated. It is simply a matter of selectively sacrificing relatively unimportant descriptions.
Washing Stage: Cleaning and removing impurities, using floatation method to separate floaters.
This stage is relatively straightforward, where the coffee beans are washed with water to remove impurities and floaters. There are rarely any special methods used for coffee beans, so there is not much specific description needed. Knowing that this process exists is sufficient.
Processing Stage: Removing unnecessary parts.
During this stage, the coffee fruit undergoes preliminary processing to remove unwanted parts. This is a crucial stage in coffee bean processing, which mainly divides into three main systems: washed, natural, and honey-processed. The classification depends on the condition of the fruit as it enters the drying stage, and the rules are as follows:
- Natural: Keeping the fruit intact.
- Honey-processed: Removing the skin and pulp, retaining the mucilage, parchment, and seeds.
- Washed: Retaining only a small amount of mucilage, parchment, and seeds.
It is easy to confuse this stage with the drying stage since washed coffee beans can also be sun-dried. The difference lies in what remains during the drying process, which is only the parchment and seeds.
Thus, you might come across descriptions like "[Sun-dried, honey-processed]" which means the coffee beans were sun-dried, and during drying, they still had mucilage, parchment, and seeds.
These are fundamental pieces of information that need to be labeled on coffee bean bags, making it easy to identify the processing method of the beans.

Fermentation Stage: Where Creativity Comes into Play for Different Roasters
The fermentation stage has a tremendous impact on the flavor of coffee beans, and in recent years, many roasters have been investing in research to explore its potential. The long and detailed descriptions in the processing methods are often related to the fermentation stage, which is a complex process. To understand how fermentation affects coffee flavor in-depth, I have written a separate article explaining the magic of fermentation in coffee processing. You can refer to it through the link below if interested.
Fermentation! The Magical Process that Gives Coffee Beans Unique Flavor – An Essential Step in Coffee Processing
Here, let me help you decipher some common descriptions related to fermentation, so when you are referring to specialty coffee bean listings, you can quickly identify the flavor profile you desire. The fermentation stage can be divided into three main aspects:
- Use of Specific Microorganisms or Yeast The choice of different microorganisms or yeast during fermentation produces varying flavors. To improve the quality of coffee beans, some roasters add specific microorganisms or yeast. However, if it is not explicitly stated, it does not mean that no microorganisms are involved. Microorganisms are abundant in the environment and play a crucial role in natural fermentation. So even without intentional addition, microorganisms attached to the coffee fruit will perform fermentation.
When you see descriptions with yeast or enzyme references, you'll know that the coffee beans have undergone fermentation with specific microorganisms.
- Anaerobic vs. Aerobic Anaerobic processing has gained popularity in recent years. Under anaerobic conditions, lactic acid bacteria replace acetic acid bacteria during fermentation, resulting in a softer acidity and improved sweetness. In anaerobic fermentation, yeast can efficiently produce aromatic compounds. As a result, more coffee bean processing methods are adopting anaerobic techniques. Anaerobic methods can be done in various ways, but most involve a sealed container filled with carbon dioxide. So, when you see the following descriptions on the coffee bean bags, they indicate that the coffee was fermented under anaerobic conditions:
Carbonic maceration
Anaerobic washed
Anaerobic sun-dried
Double anaerobic
- Additives and Ingredients Fermentation allows for intriguing chemical reactions between additives and coffee beans, leading to unique flavors. In recent years, roasters have been experimenting with adding different natural ingredients during fermentation, such as fruits, mint, or even spices, to give the coffee beans distinctive flavors. As a result, you may come across the following processing method descriptions:
Pineapple special fermentation
Mint honey process
Cinnamon honey process
Drying Stage: The Process of Reducing Coffee Bean Moisture Content
In order to prolong the shelf life of coffee beans, processing plants dry the coffee beans to a moisture content of around 12%. The drying speed and method significantly influence the flavor of the coffee beans. If dried too quickly, uneven drying may occur, while drying too slowly may lead to mold formation. Therefore, this process is often described in the processing methods. Common descriptions include:
Sun-dried
Slow drying 72-hour drying
Single-layer drying
African-style sun-dried
The Relationship Between Coffee Processing Methods and Flavors
Although the flavor of coffee beans can only be determined by tasting, the descriptions of the processing methods can provide some insights. Understanding the relationship between coffee processing methods and flavors can help us quickly find the flavors we may prefer from a long list of specialty coffee beans. Let's link the classification system with the flavors:
- Relationship between Processing Methods and Flavors Different processing methods retain different parts of the fruit, and the more elements involved in fermentation, the more complex the flavor. You can use this method to judge the possible flavor of the coffee beans. Water-washed processing has the fewest elements involved, resulting in high cleanliness and relatively low fermentation level and complexity. Sun-dried processing involves the most elements, resulting in generally higher fermentation levels and higher complexity. Honey processing falls between the two, so you can start selecting the appropriate coffee bean processing method based on your preference.
| Cleanliness | Fermentation Level | Complexity | |
| Washed | High | Low | Low |
| Honey | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Natural | Low | High | High |
- Relationship between Fermentation Stage and Coffee Bean Flavors Fermentation is a crucial stage that imparts flavor to coffee beans, so the more fermentation steps, the more complex the flavor usually. However, unlike processing methods, the relationship between the fermentation stage and coffee bean flavors is more challenging to define because it depends largely on the techniques used during production. Still, we can attempt to connect the flavors. Whether to add specified yeast has a significant impact on cleanliness since fewer types of microorganisms are involved in fermentation, resulting in lower flavor complexity. The fermentation level will depend on the actual fermentation time.
Anaerobic treatment produces more alcohol substances, resulting in higher complexity in flavors, and it generally involves a longer fermentation time, so the fermentation level is usually higher. Still, it depends on the specific situation.
The presence of additives will definitely impact cleanliness as the elements involved in fermentation increase, and the complexity is raised. The fermentation level will also depend on the actual circumstances.
| Cleanliness | Fermentation Level | Complexity | |
| Adding Yeast | High | Determined by fermentation time | Low |
| Anaerobic | Low | High | High |
| Additives | Low | Determined by fermentation time |
High |
- Relationship between Drying Stage and Coffee Bean Flavors Too fast drying may result in uneven moisture content, while too slow drying may cause defects due to microbial activity, so slow drying results in higher fermentation levels and complexity compared to other drying methods.
The drying environment also influences the flavor. Traditional methods of spreading coffee beans on the ground for drying may introduce more impurities and lower cleanliness, while raised-bed drying can produce higher cleanliness in coffee flavors.
| Cleanliness | Fermentation Level | Complexity | |
| Slow Drying | Varies | High | High |
| Traditional Drying | Low | Determined by drying time | High |
| Raised-bed Drying | High | Determined by drying time |
Low |
So, when you see two coffee bean bags labeled as "Anaerobic Water-Washed Processing" and "Anaerobic Sun-Dried Processing," you can determine that the sun-dried processing method will have higher complexity and fermentation level than anaerobic water-washed. If it is "Passion Fruit Anaerobic Sun-Dried Processing. 150 Hours of Fermentation," this coffee bean, which adds passion fruit and includes the fermentation time, may be even more complex than anaerobic sun-dried.
Please note that the above is only the correlation between processing methods and flavors, and it is a basic judgment for you when you have a list of specialty coffee beans. The flavor of coffee is significantly influenced by the roasting technique and degree, so the above table is for reference only and does not represent the absolute value of coffee bean flavors.




